- April 23, 2024
- Marketing Department
- 0
Introduction to Cloud Deployment Models
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly leveraging cloud technology to streamline their operations and enhance their competitiveness. Cloud deployment models offer organizations the flexibility and scalability they need to meet their unique requirements. Understanding the different cloud deployment models is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about their cloud strategy. This comprehensive overview delves into the top 4 cloud deployment models, providing insights into their features, benefits, and considerations.
Public Cloud Deployment Model
The public cloud deployment model is perhaps the most well-known and widely used model. In this model, cloud services are provided by third-party providers and made available to multiple clients over the internet. Public clouds offer a range of services, including infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). This model is highly scalable, cost-effective, and eliminates the need for organizations to manage and maintain their own infrastructure. However, it also comes with some potential drawbacks, such as limited customization options and concerns about data security and privacy.
Private Cloud Deployment Model
Unlike the public cloud, the private cloud deployment model is dedicated to a single organization. It is built on infrastructure that is solely used by that organization and can be located on-premises or hosted by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer enhanced security, control, and customization options compared to public clouds. Organizations that handle sensitive data or have strict compliance requirements often opt for private clouds to maintain greater control over their infrastructure and data. However, private clouds can be more expensive to set up and maintain, and they may not offer the same level of scalability as public clouds.
Hybrid Cloud Deployment Model
The hybrid cloud deployment model combines the best of both public and private clouds. It allows organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud while maintaining control over critical data and applications in a private cloud. With a hybrid cloud, organizations can seamlessly move workloads between public and private
environments based on their specific needs. This model is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating workloads or specific compliance requirements. However, it also introduces complexities in terms of data integration, security, and vendor management.
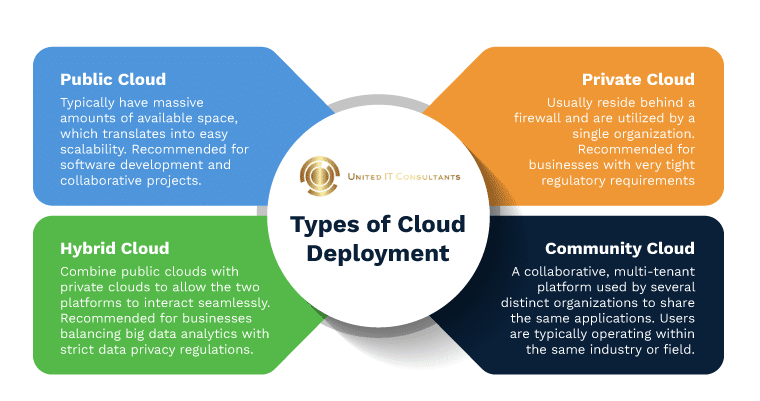
Community Cloud Deployment Model
The community cloud deployment model is a specialized form of the private cloud that is shared by a specific community of organizations with similar interests or requirements. It offers the advantages of a private cloud, such as enhanced security and control, but at a lower cost as the infrastructure is shared among community members. Community clouds are often used by organizations in sectors such as healthcare, finance, or government, where industry-specific compliance and security requirements are paramount. Collaboration and resource sharing among community members further enhance the benefits of this model.
Comparison of the Top 4 Cloud Deployment Models
When choosing a cloud deployment model, organizations must carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements. A comparison of the top 4 cloud deployment models can help businesses make an informed decision:
1. Scalability: Public clouds offer near-limitless scalability, while private clouds and community clouds have more limited scalability. Hybrid clouds provide scalability by allowing organizations to scale workloads between public and private environments.
2. Cost: Public clouds are generally the most cost-effective option, as organizations only pay for the resources they use. Private clouds and community clouds can be more expensive due to the investment in infrastructure. Hybrid clouds offer cost optimization by allowing organizations to use the public cloud for non-sensitive workloads.
3. Security: Private clouds and community clouds provide enhanced security and control compared to public clouds. Hybrid clouds require careful planning and robust security measures to ensure data protection and compliance.
4. Customization: Private clouds and community clouds offer greater customization options compared to public clouds. Hybrid clouds allow organizations to customize their private cloud environment while leveraging the public cloud for standard services.
Ready to unlock the full potential of cloud services for your business?
Let’s get you started today!
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cloud Deployment Model
Selecting the most suitable cloud deployment model requires careful consideration of various factors. Organizations should evaluate the following aspects:
5. Data sensitivity: The level of security and control required for handling sensitive data is a crucial consideration. Organizations dealing with highly sensitive data may prefer private or community clouds.
6. Compliance requirements: Different industries have specific compliance regulations. It is important to ensure that the chosen cloud deployment model aligns with these requirements.
7. Scalability needs: Organizations with fluctuating workloads should choose a cloud deployment model that provides the required scalability without compromising on performance.
8. Budget: Cost is a significant factor when choosing a cloud deployment model. Organizations should analyze their budget and consider the long-term costs associated with each model.
Case Studies of Organizations Using Different Cloud Deployment Models
Examining real-world examples of organizations using different cloud deployment models can provide valuable insights into the benefits and challenges associated with each model.
Case Study 1: Company X
Company X, a multinational corporation, opted for a public cloud deployment model to support its global operations. By leveraging the public cloud’s scalability and cost-effectiveness, Company X was able to rapidly deploy new services and expand its infrastructure as needed. The public cloud’s wide range of services also allowed Company X to streamline its operations and reduce IT complexity.
Case Study 2: Company Y
Company Y, a financial institution, required a highly secure and compliant environment due to its industry-specific regulations. To meet these requirements, Company Y implemented a private cloud deployment model. The private cloud enabled the organization to maintain full control over its infrastructure and data, ensuring the highest level of security and compliance. While the initial setup costs were higher compared to a public cloud, Company Y recognized the long-term benefits of enhanced security and control
Case Study 3: Company Z
Company Z, a healthcare provider, needed to share patient information securely with other healthcare organizations. To achieve this, they adopted a community cloud deployment model. By collaborating with other healthcare providers in the community cloud, Company Z was able to streamline data sharing while ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations. The shared infrastructure reduced costs for all participants, making the community cloud an ideal choice for Company Z.
Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Deployment Models
Implementing a cloud deployment model requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider:
9. Thorough evaluation: Conduct a comprehensive analysis of your organization’s requirements, including security, compliance, scalability, and budget, to identify the most suitable cloud deployment model.
10. Gradual migration: If transitioning from an on-premises infrastructure, consider a phased approach to migration. Start with non-critical workloads and gradually move more sensitive data and applications to the cloud.
11. Security measures: Implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
12. Vendor selection: Choose a reputable and reliable cloud service provider that aligns with your organization’s needs and has a track record of delivering reliable services and exceptional customer support.
Conclusion
Selecting the right cloud deployment model is a critical decision that can significantly impact an organization’s operations, security, and cost-efficiency. By understanding the features, benefits, and considerations of the top 4 cloud deployment models – public, private, hybrid, and community – businesses can make informed choices based on their unique requirements. Evaluating factors such as data sensitivity, compliance requirements, scalability needs, and budget constraints will guide organizations towards the most suitable cloud deployment model. By following best practices and learning from real-world case studies, businesses can successfully implement cloud deployment models and unlock the full potential of cloud technology.

