- June 7, 2024
- Marketing Department
- 0
Anyone who’s new to the MSP market will have a hard time understanding the broad concept that MSP is. But what’s managed services anyway? Who are MSPs? How are MSP and break-fix different? Let us clear the air. Read the complete guide to managed services we’ve put together for you.
Evolution of Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
Before discussing MSPs and their role in business, it’s important to understand their evolution. MSPs emerged from application service providers (ASPs) in the 1990s, which pioneered remote application hosting. An MSP provides IT infrastructure and end-user systems maintenance and operation from a remote location.
ASPs laid the groundwork for cloud computing services and organizations dedicated to remote IT support. Initially, MSPs focused on remote monitoring and management (RMM). Over time, they expanded their services to include service-based models to differentiate themselves from other MSPs.
So, how does an MSP function, and what do its operators do?
What is an MSP?
An MSP is a third-party firm that manages a client’s IT infrastructure and maintains end-user systems. Small and medium-sized businesses, nonprofits, and government bodies contract MSPs for daily tasks such as network management, infrastructure maintenance, security, and supervision.
List of services offered by MSPs
MSPs provide regular management services, allowing companies to focus on their core operations without worrying about system outages or service discrepancies. Typically, MSPs use a proactive subscription model for their services.
1. Network Handling
– Management and optimization of network infrastructure.
– Ensuring reliable connectivity and performance.
– Troubleshooting network issues.
2. Infrastructure Management
– Overseeing the entire IT infrastructure.
– Implementing upgrades and maintaining systems.
– Ensuring infrastructure scalability and reliability.
3. Inventory and Hardware Management
– Tracking and managing IT assets.
– Ensuring hardware is up-to-date and functioning properly.
– Planning for hardware refresh cycles.
4. Cybersecurity
– Implementing security protocols and measures.
– Monitoring for and responding to security threats.
– Conducting regular security assessments and updates.
5. Software Subscription Management
– Managing software licenses and subscriptions.
– Ensuring compliance with software agreements.
– Updating and renewing software subscriptions.
6. Hardware Health Monitoring
– Regularly checking the status of hardware components.
– Predicting and preventing hardware failures.
– Conducting routine maintenance.
7. Data Storage
– Providing secure and scalable data storage solutions.
– Managing data backups and recovery processes.
– Ensuring data accessibility and integrity.
8. Remote Firewall Administration
– Configuring and managing firewalls remotely.
– Monitoring and updating firewall rules and policies.
– Ensuring network security through firewall management.
MSPs can specialize in specific IT areas, such as data storage, or in vertical markets like legal, financial, healthcare, or industrial sectors. For example, managed security service providers focus on services like remote firewall administration and security as a service, while managed print service companies handle printer maintenance and supplies.
Get the plan, resources, and expertise in IT to move your business forward.
Let’s get you started today!
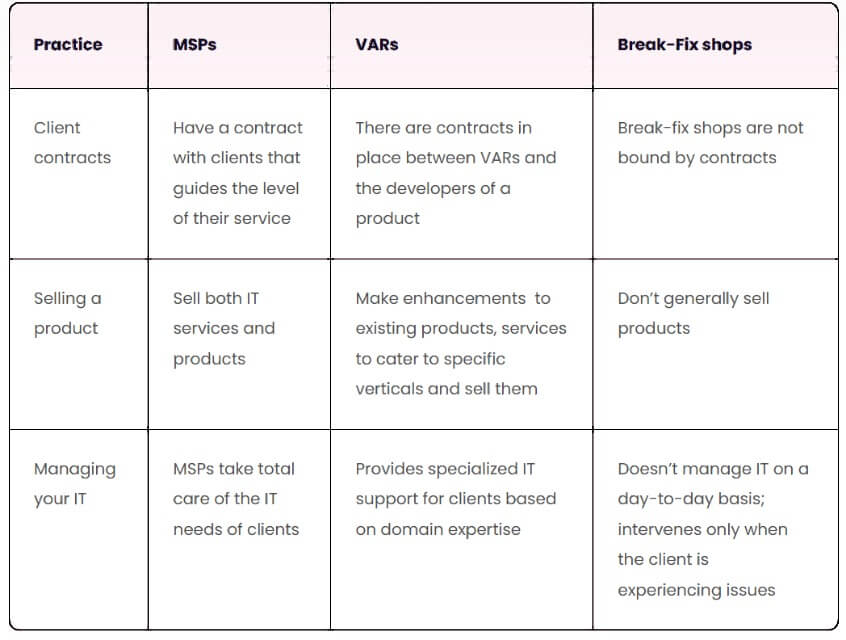
MSPs, VARs, Break-Fix shops- What’s the difference?
As with every vertical, MSPs come in various shapes and sizes. Here’s a list of service providers, based on how they operate:
MSPs have a distinct business model compared to value-added resellers (VARs), offering various pricing options like per-device, per-user, or all-inclusive models.
SMBs are aware of the cost and technical advantages of outsourcing IT services, which is more affordable than hiring an in-house team. MSPs provide a team of skilled IT professionals and offer:
– Guaranteed uptime: Ensuring top performance and reliability.
– Savings in IT costs: Reducing IT expenses and providing realistic budgets.
– Help maintaining client relationships: Fostering productive business partnerships.
– Cybersecurity: Delivering high-quality IT protection and security.
Companies that have benefited from managed services providers (MSPs) have seen immediate benefits, reduced instances of failures, improved staff productivity, a significant decrease in IT support expenses, and enhanced profitability.
How Does an MSP Work?
An MSP supports small to medium-sized businesses lacking an in-house IT staff by maintaining and servicing their IT infrastructure to ensure business continuity.
For example, a modest-sized accounting firm must handle daily financial statements and maintain secure, centralized digital records. They also need to keep their IT infrastructure running smoothly to ensure accounting applications are always operational. Managing these tasks can be challenging alongside core business activities.
An MSP can help by securely storing financial data on a centralized server and providing on-site tech support as needed.
How do MSPs make revenue?
The subscription model is the second most popular form of service business. On a monthly basis, businesses compensate an MSP with a regular charge to provide IT services.
If something goes wrong while clients are in the subscription period, the MSP will send a technician to fix it without charging a fee to the customer because the company’s subscription fee covers the repair cost. Payment plans for this type are often structured around per-hour rates per device or break-fix contracts.
The MSP also concentrates on the deployment of specialized software tools that automate various functions. These platforms are made up of remote monitoring and management (RMM) applications and professional services automation (PSA) tools:
RMM allows MSPs to maintain networks, end-user systems, servers, and mobile devices using remote management and monitoring software. Additionally, MSPs can leverage these tools to apply patches, run scripts, and install system updates to their clients’ computers.
PSA solutions enable managed service providers to supervise a company’s projects, handle accounts, and take charge of assets and inventories.
RMM tools enable MSPs to troubleshoot and monitor client network assets remotely. A quality RMM solution provides:
– Remote access and support
– Patching and scripting capabilities
– Asset management
– Alert management
PSA, or Professional Services Automation, is a tool suite that empowers managed service providers to manage client requests within a unified platform. A robust PSA system includes features such as contract management, ticket assignment, worklog management for resource tracking, automation, and efficient project management. Additionally, PSAs aid in effective client relationship management.
Most MSPs are required to offer end-user assistance, prompting PSAs to integrate helpdesk tools alongside team management applications. These self-service systems aim to reduce reliance on human intervention.
Get the plan, resources, and expertise in IT to move your business forward.
Let’s get you started today!
A comprehensive PSA should include modules for:
– Helpdesk
– Contracts
– Invoicing
– CRM
– End-user ticket logging interface
– Reporting
– Project management
PSA plays a vital role in an MSP’s tech stack, as highlighted by Chris Timm’s discussion on its significance.
Now that you understand how MSPs work, let’s address the big question: Why does your business need one? Here are six reasons to consider:

